Lyme disease affects children more than any other age group, but the young ones are often difficult to diagnose, especially before they’ve developed the vocabulary to describe how they’re feeling. To help parents recognize symptoms and prevent serious illness, I chatted with Charlotte Mao, MD, a pediatric infectious disease physician who trained at Harvard Medical School and Boston Children’s Hospital, and practiced at The Dean Center for Tickborne Illness, Spaulding Hospital, where she treated children with complex Lyme disease. She currently serves as the Curriculum Director for Invisible International’s Medical Education Initiative. Here are some frequently asked questions that she encounters in her practice.
Q: What do I do if I find a tick on my child?
If you see a tick embedded in your child, position a fine-tipped tweezer where the tick’s head meets the skin, then swiftly pull it straight out. Do not grasp, squeeze, or twist the tick’s body. Then place it in a plastic baggie with a small piece of damp paper towel. Wash the extraction area and your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
Consider sending the the tick to a testing lab, to identify the species and what microbes are inside of it. Because the current Lyme disease screening tests are unreliable in the first few weeks after a bite (it takes this long for humans to develop antibodies that can be measured), the results might provide your physician with useful information, especially if your child later comes down with symptoms. You can also go online to identify which tick species transmit various disease agents. Lyme disease is carried by blacklegged ticks, Ixodes scapularis in the Eastern United States and Ixodes pacificus in the West.
Some experts say that it takes at least 36 hours for an attached tick to transmit Lyme bacteria to a host, because this is the minimum time it takes for these bacteria to travel from a tick’s midgut to its saliva glands. However, transmission can happen in some cases with a shorter duration of attachment, specifically when bitten by a partially fed tick that already has Lyme bacteria in its saliva from a previous attachment. This occurs in about 5 to 10 percent of infected ticks, according to the Lyme bacteria discoverer, Willy Burgdorfer. Other tick-borne microbes, such as the potentially deadly Powassan virus, can be transmitted in as little as 15 minutes after tick attachment.
Time is of the essence in preventing serious tick-borne disease. So, in Lyme endemic areas, I personally advise parents to begin preventative antibiotic treatment before tick testing results come back, within 48 to 72 hours of attachment. Over the following month, closely observe a child for symptoms, such as an expanding skin lesion at the bite site, fever, malaise, headache, mild neck stiffness, aches/pains in muscles, or joints aches. If these develop, visit your pediatrician.
Q: How can I tell if my child has Lyme disease?
Early signs of Lyme disease include flu-like symptoms, such as fever (often mild), chills, head and neck pain, body aches (muscle and joint), malaise, and fatigue. (Unfortunately, these symptoms can be mistaken for irritability or viral infections, such as the flu or COVID. Check your child for a Lyme disease rash and don’t forget to check the scalp and skin-fold areas (groin, armpits, behind the knees, and ears). Not everyone gets the classic “bulls-eye” rash; an expanding rash without central clearing is more common. You can find some sample rash images on the Internet.
Other classic Lyme manifestations that can develop include a weakness or paralysis of facial muscles (Bell’s palsy); intense headaches, numbness, tingling, or weakness in extremities (neuropathy); eye and heart issues (especially cardiac rhythm abnormalities); and joint swelling or pain. Gastrointestinal symptoms, generally underappreciated as potential Lyme manifestations, may include nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, loss of appetite, gastroparesis (stomach paralysis), and/or constipation.
Q: What are some of the late-stage Lyme symptoms?
Physical complications can involve the joints, nervous system, and eyes. Lyme arthritis most commonly involves one or a few large joints, especially the knee, but can also affect the jaw (temporomandibular joint or TMJ), and, occasionally, small joints of the fingers and toes. Fatigue and aches/pains are common in late and early disease. Lyme disease can also cause behavioral or mood changes in children. Some children develop neuropsychiatric manifestations such as anxiety, depression, panic attacks, or obsessive-compulsive disorders. All these symptoms can come and go, and this can be confusing to a patient, their family, and teachers. But trust that you know your child best, and if you suspect Lyme, visit your pediatrician.
Q: What are the best Lyme disease tests?
A Lyme disease diagnosis ultimately needs to be made based on a multifaceted clinical evaluation with lab work viewed as supportive (or not), but not definitive. My diagnosis is based on a comprehensive medical history, a physical exam, and diagnostic testing for other potential explanations besides Lyme disease.
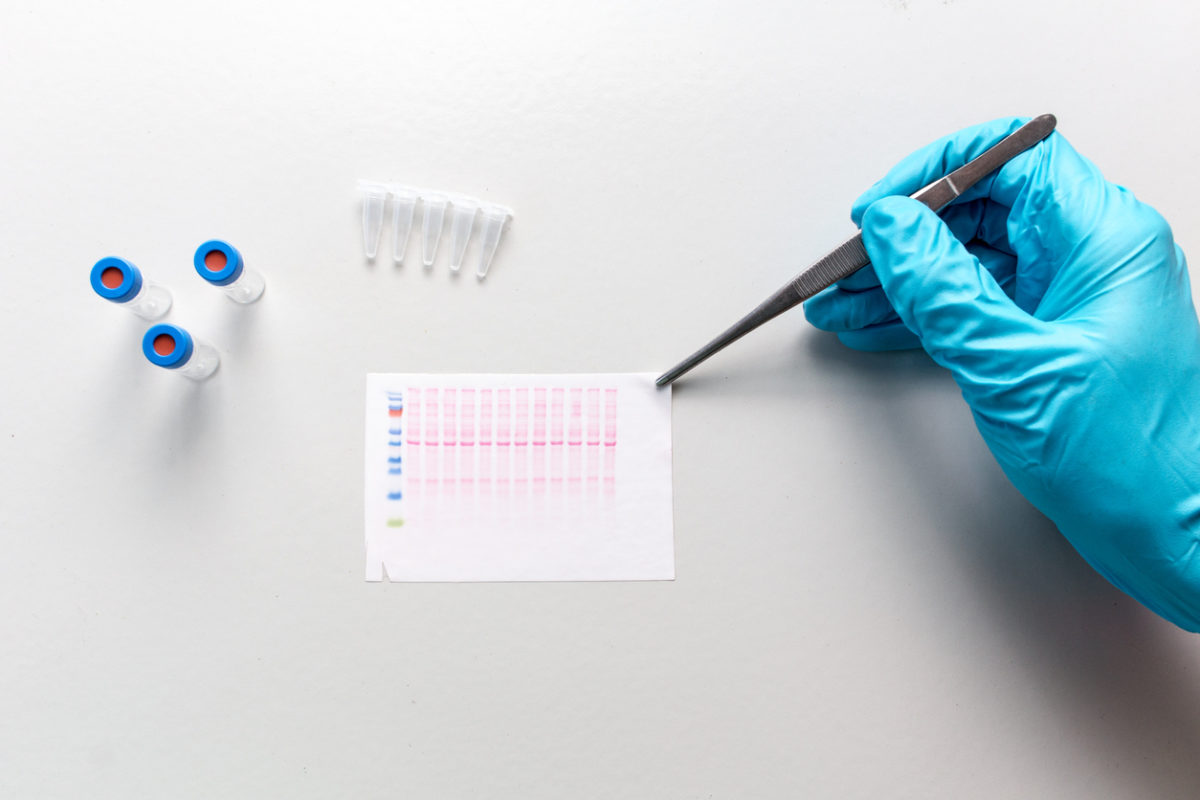
In testing, I prefer to use Lyme specialty labs that provide more diagnostic information than standard commercial labs. I particularly like Medical Diagnostics Laboratory (MDLab.com) for Lyme immunoblot testing. Immunoblots detect the presence of antibodies to specific proteins of a microorganism that develop after a person has been exposed to a target infectious organism. Once detected, these antibodies can be seen as dark bands on a blotting membrane or an imaging system. MDLab’s immunoblot reports include detection results for more than the 10 CDC-specified Lyme bands, and a photo of the patient’s actual blot with an objective optical density score grading the intensity of each detected band. In some cases, fainter bands that do not meet the lab’s positivity threshold still might provide useful clinical information, increasing the suspicion of a past or present Lyme infection.
Q: What’s your treatment approach for young children?
As an infectious disease specialist, I typically see children who’ve already been treated by their pediatrician but have continuing symptoms after standard treatment courses. These more complex cases often require individualized management approaches.
If a child has not yet received an initial antibiotic course for Lyme disease, I start with recommended oral antibiotics—doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime. (While doxycycline has traditionally not been prescribed for children under 8 years of age due to concerns of dental staining, studies have shown the risk of dental staining is much less with doxycycline than older tetracyclines. The American Academy of Pediatrics now says doxycycline can safely be used in children under 8 years for short durations, up to 21 days. Notably, doxycycline has long been the treatment of choice, regardless of age, for tick-borne rickettsial diseases such as Anaplasma, Ehrlichia, and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever.
For acute central nervous system issues such as Lyme meningitis, I prescribe recommended intravenous antibiotics (typically ceftriaxone), which more effectively reaches therapeutic drug levels in the brain and central nervous system. I also use intravenous ceftriaxone for Lyme arthritis when symptoms haven’t resolved after two courses of oral antibiotics.
To avoid gut issues, I prescribe probiotics and monitor for adverse effects such as diarrhea.
Q: What if symptoms continue after treatment?
In the U.S., ticks are known to carry 18 or more disease-causing microbes, and sometimes concurrent infections can cause lingering symptoms, even after recommended Lyme disease treatment. A considerable degree of overlap exists among the nonspecific manifestations of Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections, but there are certain symptoms that are more prevalent for specific co-infections. I routinely test for Bartonella, Babesia, Anaplasma/Ehrlichia, and Borrelia miyamotoi if the child has not already had this testing done.
Bartonellosis, an under-recognized bacterial infection that can be transmitted by fleas, lice, or cat scratches/bites, can cause a multitude of symptoms, some of them overlapping with those of Lyme disease. These might include fever; swollen lymph nodes; an enlarged liver or spleen; skin “tracks” that may resemble striae or stretch marks; “evanescent” rashes that come and go; and neuropsychiatric symptoms, especially anxiety, panic attacks, anger/aggression/rage episodes, and obsessive-compulsive disorders. Other potential symptoms include tremors; jerky movements; sudden muscle weakness (e.g., “legs giving way”); a sensation of internal vibration; seizures; musculoskeletal pain, including in soles of the feet or shins (the latter is a reported feature of trench fever, caused by Bartonella quintana); abdominal pain; and eye issues (including uveitis and retinitis, both also seen with Lyme). Lab findings occasionally seen with Bartonella, all typically mild, include decreases in white blood cell count; increased eosinophils or monocytes; hemolytic anemia (rarely); increased C-reactive protein levels; and liver enzyme elevations.
Common babesiosis symptoms, caused by a parasite that infects red blood cells, include night or day sweats, fevers (can be high), chills, fatigue, malaise, hemolytic anemia and low platelets. Less common symptoms include headache, dry cough, shortness of breath (sometimes described as “air hunger”), nausea, abdominal pain, vomiting, and diarrhea.
The combination of low white blood cell and platelet counts make me suspect Anaplasma or Ehrlichia.
I always ask about factors that increase risk for repeat exposure/infection, such as outdoor hobbies (hiking, camping, gardening) and exposures to animals and blood-sucking bugs such as ticks, fleas, and lice. For the child with persistent symptoms after recommended treatment regimen(s), I also explore the possibility of nutritional/vitamin deficiencies or environmental toxic exposures, such as water-damaged buildings with mold contamination. Mold toxins or mycotoxins, produced by certain mold species, can complicate Lyme disease or co-infections by causing overlapping symptoms or negatively impacting treatment response.
The decision to administer additional antimicrobial therapy in patients with persistent or recurrent symptoms following standard treatment for Lyme disease is a controversial issue. According to treatment guidelines of most major medical societies, there is no good evidence that these persistent “post-treatment” symptoms are driven by an active infection that might benefit from additional antimicrobial therapy. The topic is too complex to cover here, but I’ll say simply that I do not agree with this blanket statement. The question of how best to treat this subgroup of patients is an area that requires more research and funding.
Q: I’m pregnant. Can I pass Lyme disease to my unborn child?
Borrelia infections can be transmitted from a pregnant mother to her infant. How frequently this occurs and the range of potential health risks for the infant/child have not been well-established. Studies to-date indicate significantly fewer adverse outcomes in treated compared to untreated pregnant women. This is another area that has been under-studied and requires more research attention and funding.
Q: I’m sending my kids to summer camp. Any advice on keeping them safe?
I recommend pre-spraying clothing with permethrin to keep ticks away. This typically remains effective for six to eight washings. Have them pack insect repellents and don’t forget to teach them how to do tick checks.
Q: What resource can I give my child’s pediatrician to learn more about tick-borne illness?
Invisible International has created the first-ever continuing medical education platform that focuses on tick-borne illness. It is accredited by the American Academy of Family Physicians. Courses on this platform are available at no cost to physicians and other providers. Learn more and share this with your child’s pediatrician. Invisible’s Medical Education Initiative is supported by the Montecalvo Foundation.
###